Your Guide to Major Geopolitical & Security Hotspots
Today, only 11 countries out of 162 tracked by the Institute for Economics and Peace are free from conflict. This reality shapes our world in ways we might not fully understand. The number of nations facing extreme or high political risk has risen from 32.5% to 36.5% in over a decade, according to Maplecroft’s Political Risk Index.
We live in a time where major geopolitical & security hotspots fill our headlines every day. Charles Hecker, a research director at Control Risks, says we are in a period of exceptionally high geopolitical activity and violence. These tensions affect millions of people living in conflict zones.
Current conflicts & humanitarian crises are found on every continent. Nations compete for control and influence over valuable trade routes and resource-rich territories. The BlackRock Geopolitical Risk Indicator uses advanced machine learning to track how markets respond to these risks. It shows which hotspots really impact global stability.
To understand today’s world, we must grasp these flashpoints. Each conflict zone has its own history, players, and stakes. Some disputes have been ongoing for decades, while others break out suddenly. The humanitarian impacts of these conflicts affect food security, energy prices, and refugee movements, impacting areas far beyond the conflict zones.
Key Takeaways
- Only 11 out of 162 countries remain uninvolved in any form of conflict according to the Institute for Economics and Peace
- Political risk levels have increased significantly with 36.5% of nations now classified as extreme or high risk
- The BlackRock Geopolitical Risk Indicator tracks market reactions to global tensions using machine learning analysis
- Major trade routes worth $5 trillion annually pass through contested waters and territories
- Resource competition drives many territorial disputes from the Arctic to the South China Sea
- Humanitarian crises from these conflicts affect global food security and create massive refugee movements
Understanding Major Geopolitical & Security Hotspots in Today’s World
We live in a world where global tensions change markets and nations every day. Political hotspots come from deep territorial disputes, fierce competition for resources, and old historical grievances. These areas are key because they affect everything from energy prices to trade routes.
The Rising Complexity of Global Political Tensions
Today’s conflicts have many layers of security that didn’t exist before. Governments fight with big companies over borders and who’s in charge. Companies like Apple and Samsung work across disputed areas, but countries defend their borders more than ever. This creates a big problem between business and national security.
Civil unrest has hit markets that were once stable. Brazil is facing big political problems, Bulgaria is protesting corruption, and Turkey is dealing with democracy and authority issues. Big countries are making things worse by supporting different sides in these disputes.
How Market Attention Reflects Geopolitical Risk Levels
Financial groups watch political risks closely. BlackRock’s Geopolitical Risk Indicator looks at reports and news to see how worried investors are. When reports talk about a conflict a lot, it means investors are really worried about that area’s stability.
Why Territorial Disputes and Resource Competition Drive Conflicts
Not having enough resources leads to conflicts today. The Arctic is a big example because melting ice shows oil and shipping lanes worth trillions. Russia, Canada, and the US are fighting for control while also trying to rebuild other areas.
South China Sea Conflict: The Maritime Crossroads of Global Trade
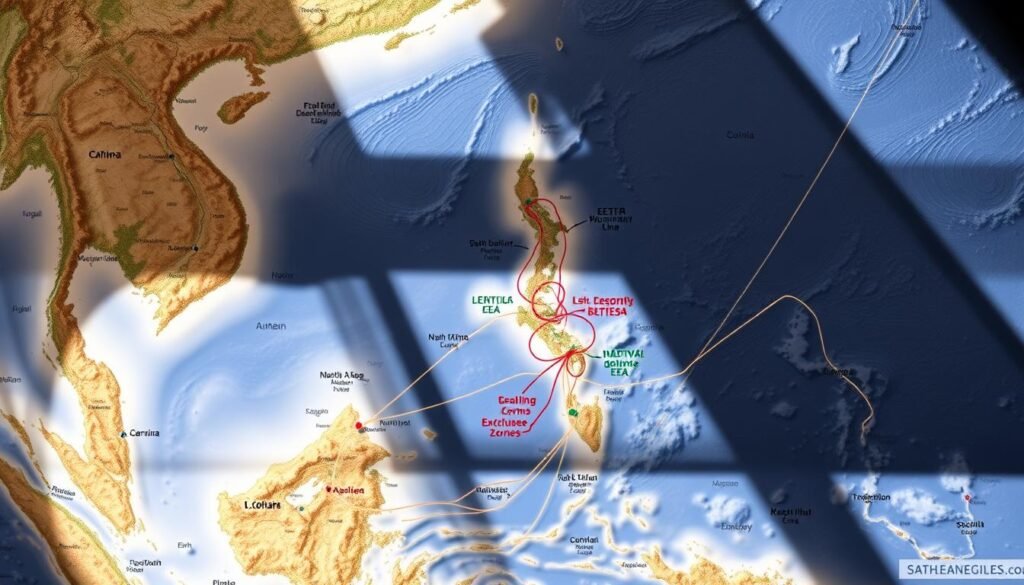
The South China Sea is a hot spot in the world, with many countries fighting over it. Over $5 trillion in trade moves through this area every year. This makes the maritime disputes very important for the world’s economy. China, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei, and Taiwan are all fighting over islands and waters.
Overlapping Territorial Claims Among Multiple Nations
There are six countries fighting over parts of the South China Sea. China claims almost 90% of the area with its “nine-dash line.” But Southeast Asian countries say this is theirs. The Philippines won a big case in 2016, saying China’s claims are wrong.
Vietnam says it has been using the waters for a long time. It’s close to the Paracel and Spratly Islands.
Natural Resource Competition and Military Escalation
Under the sea, there’s a lot of oil and gas. China has built military bases on artificial islands in the Spratlys. Other countries have smaller bases.
Impact on $5 Trillion Annual Trade Routes
The South China Sea is key for global trade. One-third of all sea trade goes through it. Changes in alliances can affect shipping routes to Europe, Africa, and the Middle East.
Any problem here could hurt energy supplies to Japan, South Korea, and China. This could cause big economic problems worldwide.
Taiwan Strait Tensions and Cross-Strait Relations

The narrow waters between Taiwan and mainland China are a key spot in modern geopolitics. Taiwan Strait tensions affect regional stability and global economic security. The 110-mile-wide strait is both a physical and political barrier, shaping international relations in the Indo-Pacific.
China sees Taiwan as part of its territory, while Taiwan is a democratic society with its own government and military. This disagreement drives the Taiwan Strait dynamics we see today. Chinese military exercises near Taiwan have grown, with the People’s Liberation Army doing regular naval and air force activities in Taiwan’s air defense zone.
The situation also impacts US-China relations as Washington is Taiwan’s main security partner. The United States gives defensive weapons to Taiwan and keeps its military plans unclear. This balance affects:
- Global semiconductor supply chains centered in Taiwan
- Regional military alliances and partnerships
- International shipping routes through the strait
- Economic stability across East Asia
For people on both sides, dealing with trauma from decades of separation and military threats is hard. Families split in 1949 face complex emotional and political challenges. They live with the constant fear of conflict.
Russia-Ukraine War and Its Global Implications

The Russia-Ukraine war has changed the world a lot, starting in February 2022. It has affected global security, economics, and diplomacy. This conflict has made Russia’s role in the world very important and has changed European security.
We see new alliances, changes in energy markets, and fights for stable governance in some areas.
The Crimean Annexation and Eastern Ukraine Conflict
Russia took Crimea in 2014, a big change in post-Cold War Europe. Crimea is key because of its Black Sea location and the Sevastopol naval base. This gives Russia a big military advantage.
In eastern Ukraine, Donetsk and Luhansk became battlegrounds. Here, Russian-backed separatists fought against Ukrainian control.
In 2022, the conflict grew bigger. Cities like Mariupol, Bakhmut, and Kherson saw a lot of damage. But Ukraine’s fight has surprised many, who thought Russia would win fast.
NATO-Russia Relations and Regional Security Dynamics
NATO’s growth towards Russia has been a big issue for years. Now, countries like Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are part of NATO. Finland and Sweden want to join too, changing European security.
- Military aid to Ukraine exceeds $100 billion from Western nations
- NATO forces strengthened along eastern borders
- Energy dependencies restructured across Europe
- Defense spending increased in most European countries
Humanitarian Crisis and International Sanctions
The war has made millions of Ukrainians refugees, the biggest crisis in Europe after World War II. Cities are losing power, hospitals, and schools. Sanctions aim at Russian energy, banks, and tech imports.
Russia is now working with China, Iran, and North Korea for economic help. It also uses the Wagner Group in Africa to keep its influence.
Middle East Instability: From Historic Conflicts to Modern Challenges

The Middle East is a hot spot of conflict, where old issues meet new global interests. Wars and tensions shape the world’s energy markets and international ties. Its oil and key shipping lanes make it very important.
Israel-Palestine: Deep-Rooted Territorial and Identity Disputes
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a long-standing fight over land, identity, and who rules. Gaza often sees violence. Key issues include:
- The status of Jerusalem as a capital city
- Border delineation and settlement expansion
- Palestinian refugees’ right of return
- Control over water resources
Persian Gulf Tensions Between Iran and Arab States
Relations between Iran and Arab states like Saudi Arabia and the UAE are always changing. These rivalries lead to conflicts in Yemen, Syria, and Lebanon. They fight over religion, influence, and control of energy markets.
Strait of Hormuz: The Global Oil Chokepoint
The Strait of Hormuz is the world’s most important oil transit chokepoint. It carries about 21 million barrels of oil every day. This oil is 20% of what the world uses.
| Strait Statistics | Daily Volume | Global Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Transit | 21 million barrels | 20% of world consumption |
| Natural Gas | 3.5 trillion cubic feet annually | 33% of LNG trade |
| Ship Traffic | 88 vessels | Critical for Asia-Pacific |
North Korean Nuclear Threat and Korean Peninsula Dynamics

The Korean Peninsula is a hot spot in the world. The north korean nuclear threat affects security every day. The fighting stopped in 1953, but tensions flare up often. North Korea’s nuclear weapons pose a big risk, not just in Asia.
Talks between countries have had ups and downs over 30 years. We’ve seen hopes raised and dashed, from the Agreed Framework in 1994 to the Singapore Summit in 2018. Despite efforts, peace remains elusive. Unlike some African conflicts, the Korean issue is between two powerful states.
| Key Nuclear Tests | Yield (Kilotons) | International Response |
|---|---|---|
| October 2006 | 0.7-2 | UN Resolution 1718 |
| May 2009 | 2-5.4 | UN Resolution 1874 |
| February 2013 | 6-16 | UN Resolution 2094 |
| September 2017 | 100-250 | UN Resolution 2375 |
Recently, North Korea has teamed up with Russia, making talks harder. Military ties are growing, but old talks are stuck. The peninsula’s future depends on balancing deterrence with dialogue, a tough task for the world to tackle together.
Arctic Territorial Disputes in a Changing Climate
The Arctic is changing fast. Rising temperatures and melting ice open up new resources worth trillions. Nations are fighting over these riches, like oil, gas, and minerals needed for tech and green energy.
New Shipping Routes and Resource Access
The Northern Sea Route is now open longer than before. It cuts travel time between Europe and Asia by 40%, saving fuel costs. Russia and China are building bases, showing their interest in the area. This mirrors the global tech race, where resources are key.
Competing Claims Among Arctic Nations
Eight countries claim parts of the Arctic. Russia wants 1.2 million square kilometers of seabed. Canada and Denmark fight over Hans Island. The US disputes Canada’s claim on the Northwest Passage. These disputes are like the strategic moves in the Indo-Pacific, where control equals power.
Environmental Concerns and Indigenous Rights
Indigenous peoples face big changes in their homes. The Inuit, Sami, and others want a say in their lands. More shipping and mining harm the environment. We must find a balance between growth and protecting the Arctic for all.
Sahel Region Terrorism and Sub-Saharan Security Challenges
The Sahel region is facing a growing security crisis. This crisis threatens stability in West and Central Africa. Terrorist networks are expanding, reaching from Mali and Burkina Faso to Nigeria and Sudan.
These groups use weak governance, poverty, and ethnic tensions to gain power. They establish strongholds in remote areas.
Boko Haram is a major threat in the region. They mainly operate in northeastern Nigeria but can strike anywhere. Their actions destabilize Chad, Niger, and Cameroon.
The rise of far-right political movements adds complexity. These groups push for policies that divide people. Military coups, backed by populist ideas, are becoming more common in Mali and Burkina Faso.
- Al-Qaeda affiliates control vast territories in northern Mali
- Islamic State franchises operate across the Lake Chad Basin
- Armed groups exploit gold mining sites for financing
- Cross-border attacks displace millions of civilians
International investors face big challenges. Security costs have tripled in some places. Insurance premiums also reflect the high terrorism risks.
We need to tackle Sahel region terrorism with military action and development. This will help address the instability’s root causes.
Iran Nuclear Program and Regional Power Balance
The Iran nuclear program is at the heart of tensions in the Middle East. It changes alliances and how countries think about security. This issue affects oil markets and military plans, making it key to regional stability.
International Sanctions and Diplomatic Negotiations
For over a decade, sanctions have hit Iran’s oil, banking, and tech imports. This cut Iran’s oil income from $119 billion in 2011 to $53 billion in 2020. Talks in Vienna, known as the JCPOA, have seen many rounds of negotiations.
The evolving relationships between Israel Arab states and Iran have changed diplomacy. The Abraham Accords have brought Israel and the UAE, Bahrain, Morocco, and Sudan closer. This is partly because of shared worries about Iran’s influence.
Impact on Gulf Security Architecture
The future of gulf security is tied to Iran’s power and goals. Many navies patrol the Strait of Hormuz, where 21% of global oil flows. Drone attacks and tanker incidents have raised insurance costs and energy prices.
The Role of External Powers in Regional Dynamics
Big powers have a big military presence in the area. The US has bases in Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain. Russia gives S-400 air defense systems, and China is Iran’s biggest trading partner, despite trade wars and sanctions. These players shape security and diplomacy in the region.
India-Pakistan Border Disputes: Kashmir and Beyond
The India-Pakistan border disputes are a long-standing issue in South Asia. They have led to many wars and military clashes. The Kashmir region is at the center of this conflict, with both sides claiming it.
This conflict goes beyond just land. It affects the stability of the whole region. Our analysis shows that it touches every part of regional stability.
Strategic Importance and Water Resources
Kashmir is key for both countries because of its strategic location. It controls the Indus River system, which is vital for irrigation. The Indus Waters Treaty of 1960 tries to manage these shared waters.
Yet, disagreements over dams and water rights continue. This shows the ongoing tensions over water resources.
Nuclear Dimension of the Conflict
Both India and Pakistan have nuclear weapons. This makes their border disputes very dangerous. Pakistan developed nuclear weapons in 1998, after India’s tests.
This nuclear standoff makes peace efforts hard. Despite the risks, clashes along the Line of Control happen often.
| Military Assets | India | Pakistan |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear Warheads | 160-164 | 165-170 |
| Active Military Personnel | 1.45 million | 654,000 |
| Defense Budget (2023) | $81.4 billion | $10.3 billion |
Human Rights Issues and Local Insurgencies
People in the area face serious human rights issues. Armed forces and militant groups harm them. Insurgent groups like Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed add to the problem.
Civilians suffer under curfews, communication blackouts, and displacement. To protect them, we need international help. This is key to solving the India-Pakistan border disputes.
Great Power Competition: US-China Relations and Tech Rivalry
The battle between the United States and China has become a key part of our world today. This rivalry goes beyond just military strength. It also involves technology, trade, and who has influence in different areas.
The fight for semiconductors is at the core of this tech rivalry. These small chips are vital for everything from phones to missiles. They are key for both economic growth and keeping a country safe.
China buys over $300 billion worth of chips every year. The U.S. leads in chip design and making advanced equipment. This has led both countries to spend billions on making chips at home.
This rivalry is also seen in strategic alliances. The AUKUS deal between Australia, the U.K., and the U.S. is about countering China’s growing power in the Indo-Pacific. The Quad alliance, with the U.S., Japan, India, and Australia, works to keep the sea lanes open and support democracy.
China’s way of doing business is different from the West. It uses state-led capitalism, where the government guides business. This makes it hard for international companies to operate in China’s unique environment.
China’s push for more territory seems to be part of its plan to show it’s a rising power. This is happening as China’s economic influence grows, and it gets closer to Russia.
Emerging Hotspots and Future Security Challenges
New regional conflicts are changing how we see global security. They challenge NATO and international stability. These hotspots need our focus as they affect diplomacy, military alliances, and Europe’s security.
Nagorno-Karabakh: Ethnic Conflicts and Regional Alliances
The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict is a complex issue affecting regional stability. This area is internationally recognized as part of Azerbaijan but mostly inhabited by Armenians. The 2020 fighting changed who controls the territory.
This conflict impacts the Western Balkans and tests international mediation. It shows the need for careful diplomacy.
East China Sea Disputes Over Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands
Tensions between China and Japan are rising over the Senkaku/Diaoyu Islands. These islands are key for fishing and may have oil worth billions. The U.S. backing Japan adds to the tension, affecting Pacific security and EU defense talks.
Spratly Islands Militarization and Maritime Law
China’s building of military bases on artificial islands in the Spratly Islands is a big challenge to maritime law. Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei also claim parts of these islands. This militarization threatens the freedom of navigation in key shipping lanes.
Cyprus Division and Reunification Challenges
Cyprus is divided between the Republic of Cyprus and the Turkish-controlled north. This division blocks Turkey’s path to EU membership. It also affects Europe’s expansion plans.
The unresolved status causes ongoing tensions between Greek and Turkish Cypriots. It also makes energy exploration in the Eastern Mediterranean complicated.
Conclusion
We live in a world where major geopolitical & security hotspots shape business decisions and international relations daily. From the South China Sea to the Arctic, from Taiwan to Ukraine, these flashpoints demand our constant attention. Companies operating across borders must adapt to shifting regional security dynamics while preparing for unexpected disruptions.
Robert Amsterdam, an international law and political advocate, suggests that businesses maximize their online reputation and hire local staff with genuine connections. This approach helps companies navigate current conflicts & humanitarian crises more effectively. Geoff Taylor from Willis Risk Solutions emphasizes mapping supplier locations against risk assessments. This strategy reveals vulnerable points and possible supply chain bottlenecks before they become critical problems.
The era of great power competition between the United States and China adds another layer of complexity to global operations. Companies that succeed will be those that monitor existing risks while scanning for new threats. A defensive and self-reliant approach works best in unstable regions. Building strong local partnerships provides both protection and opportunity when tensions rise.
Our understanding of these major geopolitical & security hotspots continues to evolve as new challenges emerge. The companies best positioned for success combine real-time monitoring with strategic planning. They recognize that today’s regional security dynamics require both flexibility and resilience. Smart businesses prepare for multiple scenarios while maintaining the agility to respond when situations change rapidly.




